Latest Research Publications

Research 203: Environmental Flow Assessment for Irish Rivers
Authors: Katherine E. Webster, Katie Tedd, Catherine Coxon and Ian Donohue, March 2017
Year: 2017
The overarching goal of this project was to review state of the art EFlow methodology to identify alternatives most suited to the Irish context and for developing flow standards.

Investigation into the Assessment of Health Impacts within National Environmental Regulation Processes
Report commissioned by the Environmental Protection Agency, March 2017
Year: 2017
In 2013, the EPA commissioned Golder Associates to undertake a study into how human health impacts are dealt with throughout the European Union (EU) by environmental regulators with an emphasis on the role of health impact assessment (HIA) at the planning / environment interface.

Research 200: Health and Water Quality Impacts Arising from Land Spreading of Biosolids
Authors: Mark G. Healy, Owen Fenton, Enda Cummins, Rachel Clarke, Dara Peyton, Ger Fleming, David Wall, Liam Morrison and Martin Cormican, January 2017
Year: 2017
Research Report 200 detailing the Health and Water Quality Impacts Arising from Land Spreading of Biosolids

Research 211:State of Play of Air Science Research in Ireland: Discussion Document
Authors: Aoife Donnelly, Bruce Misstear, Brian Broderick and Francesco Pilla, January 2017
Year: 2017
The purpose of this discussion document is to help identify knowledge gaps and priorities for air science research in Ireland.

Research 206: ECORISK Ecosystem Services Valuation for Environmental Risk and Damage Assessment
Authors: Craig Bullock and Robert O’Shea, January 2017
Year: 2017
ECORISK had the objective of exploring methods whereby the valuation of social and economic impacts could be used to supplement established methods of environmental damage assessment for the purposes of remediation.

Research 194: AgImpact Project: A Systematic and Participatory Review of Research on the Impact of Agriculture on Aquatic Ecosystems in Ireland
Authors: Donnacha Doody, Paul Cross, Paul Withers, Rachel Cassidy, Cara Augustenborg, Andrew Pullin, Owen Carton and Seamus Crosse, December 2016
Year: 2016
Research 194: AgImpact Project: A Systematic and Participatory Review of Research on the Impact of Agriculture on Aquatic Ecosystems in Ireland

Research 191: Delivering Integrated Catchment Management through the Bottom-up Approach: A Critical Analysis
Authors: John Ballinger, Travis O’Doherty, Fran Igoe, Catherine Dalton, Brendan O’Keeffe and Bryan Riney, December 2016
Year: 2016
Research report 191 - A Critical Analysis of Delivering Integrated Catchment Management through the Bottom-up Approach

Research 204: Irish Soil Information System: Soil Property Maps
Authors: Rachel E. Creamer, Iolanda Simo, Lilian O’Sullivan, Brian Reidy, Rogier P.O. Schulte and Reamonn M. Fealy, December 2016
Year: 2016
This report has synthesised the soil profile descriptions taken as part of the Irish Soil Information System project and developed a range of soil property maps to provide users with generalised descriptions of a range of soil properties which are relevant to soil science research and soil management advice in Ireland. The property maps include; soil texture, soil depth, soil pH, soil bulk density and soil carbon.

Research 189: Identification and evaluation of phosphorus recovery technologies in an Irish context
Authors: Michael P. Ryan, Angela Boyce and Gary Walsh, December 2016
Year: 2016
Research report 189 on Identification and evaluation of phosphorus recovery technologies

Research 195: Health Benefits from Biodiversity and Green Infastructure
Authors: Caitriona Carlin, Martin Cormican and Mike Gormally, December 2016
Year: 2016
This project reviewed (1) evidence of wellbeing and health benefits from biodiversity, (2) views of health benefits from nature held by people who make decisions regarding green space and (3) practices to engage the public with the natural environment as a sustainable health strategy, to inform policymakers and practitioners of the health benefits from the natural environment and to recommend implementation strategies in Ireland

Research 178B: Sustainability Evaluation Metric for Policy Recommendation: Technical Guidance Manual
Authors: Bernadette O’Regan, Travis O’Doherty, Brian G. Fitzgerald and Richard Moles, December 2016
Year: 2016
This Guide accompanies Research 178A: Quantitative Evaluation of Settlement Sustainability Policy

Research 178A: Quantitative Evaluation of Settlement Sustainability Policy
Bernadette O’Regan, Travis O’Doherty, Brian G. Fitzgerald and Richard Moles, December 2016
Year: 2016
This report explains a method and decision support tool designed to aid Local Authorities and communities in prioritising policies which benefit the environment and are appropriate for their circumstances.

Research 187 - ESManage Literature Review Ecosystem Services in Freshwaters
Authors: Hugh B. Feeley, Michael Bruen, Craig Bullock, Mike Christie, Fiona Kelly, Kyriaki Remoundou, Ewa Siwicka and Mary Kelly-Quinn, December 2016
Year: 2016
The ESManage Literature Review considers how the ecosystem services framework aligns with the objectives of current policy and legislation to inform management of freshwater resources.

Research Report 185: Investigation of the Implications for Ireland of Emerging Standards on Pharmaceuticals in Receiving Waters
Authors: Erin Jo Tiedeken, Eoghan Clifford and Neil J. Rowan, December 2016
Year: 2016
This report provides an understanding of the state of research on three emerging aquatic pollutants of particular legislative importance, and demonstrates the need to protect our waterways from the severe anthropogenic pressure of chemical pollutants.

Research 184: Assessing Recent Trends in Nutrient Inputs to Estuarine Waters and Their Ecological Effect
Authors: Sorcha Ní Longphuirt and Dagmar B. Stengel, December 2016
Year: 2016
Research report 184 Assessing Recent Trends in Nutrient Inputs to Estuarine Waters and Their Ecological Effect
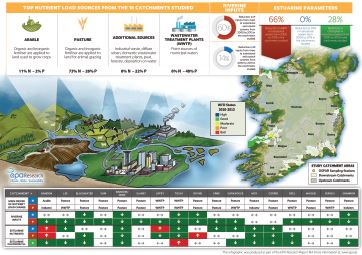
Research 184: Assessing Recent Trends in Nutrient Inputs to Estuarine Waters and Their Ecological Effect
Year: 2016
Infographic based on Research Report 184

Research 183: Assessing and Developing Natural Background Levels for Chemical Parameters in Irish Groundwater
Authors: Katie Tedd, Catherine Coxon, Bruce Misstear, Donal Daly, Matthew Craig, Anthony Mannix and Taly Hunter Williams, December 2016
Year: 2016
This report details Assessing and Developing Natural Background Levels for Chemical Parameters in Irish Groundwater

Research 181: Predicting Ecological Status in Unmonitored Lakes Using Catchment Land Use and Hydromorphological Characteristics
Authors:Caroline Wynne and Ian Donohue, December 2016
Year: 2016
The objective of the current study was to develop a method to predict the ecological status of unmonitored lakes to fulfil the requirements of the Water Framework Directive (WFD).

Research Report 180: Towards Integrated Water Management (TIMe)
Authors: Alec Rolston, Eleanor Jennings and Suzanne Linnane, November 2016
Year: 2016
The overarching objective of the Towards Integrated Water Management (TIMe) Project was to connect science, policy, managers and local communities for the integrated management of Ireland"s water resources to assist in delivering improvements in environmental status, water quality and water management.

Final Report 5: Regulatory Framework for Environmental Protection
Year: 2016
This is the Final Report 5 of the UGEE Joint Research Programme.