Latest Environment and health reports

Research 477: DESIGN – Detection of Environmental Sources of Infectious Disease in Groundwater Networks
Authors: Carlos Chique, Paul Hynds, Liam Burke, Dearbhaile Morris, Michael Ryan and Jean O’Dwyer, February 2025
Year: 2025
In Ireland groundwater sources provide domestic drinking water to approximately 750,000 people in mainly rural areas. Studies that differentiate the exposure pathways and sources are of paramount importance for establishing environmental management solutions that safeguard public health. Ireland currently has the highest incidence of verotoxigenic Escherichia coli (VTEC) infection in the EU, domestic private wells are identified as a likely source of infection. This is a public health concern for public authorities and consumers alike. The DESIGN research project provides the first quantitative assessment of VTEC and Cryptosporidium in domestic groundwater supplies in Ireland. It provides insight into the prevalence, source and transport of VTEC and Cryptosporidium in groundwater supplies. The research developed bespoke, spatio-temporal groundwater management policies, and offers invaluable guidance for future planning, remediation and mitigation of contamination in private wells.

Research 474: STEP_WISE: Spatiotemporal Epidemiology of Primary Waterborne Infections – Cryptosporidium and VTEC
Authors: Authors: Paul Hynds, Jean O’Dwyer and Martin Boudou, January 2025
Year: 2025
Ireland regularly reports the highest annual crude incidence of verotoxin-producing Escherichia coli (VTEC) enteritis and cryptosporidiosis in Europe, it is typically 5–10 times the European average. Drivers of infections include short-term hydrometeorological conditions, elevated levels of pastoral agriculture and high reliance on septic tanks and private domestic groundwater sources. Forecasts suggest that Ireland will experience significant hydrometeorological pattern changes due to global warming. The STEP_WISE project focused on increasing scientific understanding of the spatiotemporal mechanisms associated with waterborne VTEC enteritis and cryptosporidiosis in Ireland, and determining how these findings could be translated into enhanced environmental, infrastructural and healthcare policies. The research findings provide policy actors with valuable information to address transmission sources, pathways and source–pathway interactions associated with both infections in Ireland.

Research 452: Public Exposure to Non-ionising Radiation from Major Electricity Infrastructure in Ireland
Authors: Anna Mölter, Hamed Jalilian, Martin Röösli, Frank de Vocht and Francesco Pilla, March 2024
Year: 2024
Major electricity infrastructure, such as high-voltage power lines, transformer stations and substations, emits non-ionising radiation in the form of extremely low-frequency electromagnetic fields (ELF EMFs). Potential health effects associated with long-term exposure to ELF EMFs have been a concern since the late 1970s. However, epidemiological studies of health risks of ELF EMF exposure have reported varying results, and a causal relationship has not been established. This research report presents a review on the published literature in relation to populations exposure to ELF EMFs, epidemiological studies on associated health risks, current EU policies, monitoring strategies, methods to reduce exposure and strategies for risk communication.
.jpg)
Research 448: Antimicrobial Resistance and the Environment – Sources, Persistence, Transmission and Risk Management (AREST)
Authors: Dearbháile Morris, Niamh Cahill, Catherine Burgess, Enda Cummins, Finola Leonard, Brigid Hooban, Carlos Chique, Ciara Tyrrell, Shun Wang, Ciarán Monahan, Aoife Joyce, Kelly Fitzhenry, John Cullinan, Georgios Miliotis, Louise O’Connor, Deirdre Prendergast, Martin Cormican, Rita Gately, Rajat Nag, Fiona Brennan, Fiona Walsh and Xinmin Zhan, February 2024
Year: 2024
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) is recognised globally as one of the greatest challenges to human and animal health. In 2021, Ireland’s second National Action Plan on AMR (iNAP2) strengthened Ireland’s commitment to tackling the challenge of AMR using the ‘One Health’ approach. The role of the environment in the persistence and transmission of AMR is the least studied element of the One Health paradigm. This was further highlighted by the analysis commissioned by the EPA in preparation for iNAP2. The findings of the AREST project add significantly to our understanding of this environmental dimension of AMR by (1) providing evidence of the extent of contamination of the Irish environment with antimicrobial-resistant organisms and antimicrobial resistance genes of clinical concern, (2) generating national-level data on the key sources, hotspots and drivers of AMR in the environment from the human health and agriculture sectors, and (3) providing key data and recommendations.

Research 442: Impact of Nitrogen Dioxide on Health with Particular Emphasis on Vulnerable Groups
Authors: Aonghus Ó Domhnaill, Margaret O’Mahony, Brian Broderick, Martina Hennessy, Aoife Donnelly, Owen Naughton, Eimir Hurley, Philip Carthy, Anne Nolan, Frank Moriarty and Seán Lyons, November 2023
Year: 2023
Exposure to nitrogen dioxide (NO2) is associated with adverse effects on hospital admissions for various diagnoses; respiratory illnesses such as asthma, cancer, adverse birth outcomes, as well as mortality. The main source of NO2 in Ireland is road transport, particularly diesel engines. Other sources include off-road machinery, industrial and construction activities, and electricity and heat production. This research project analysed associations between the model estimations of NO2 and the health data of 8000 adults aged over 50 years. Using the HSE-PRCR prescribing database, the project found a positive association between respiratory item prescription rates and PM2.5 levels, while the results for NO2 were inconclusive. The project also developed an enhanced Wind Sector Land Use Regression (WS-LUR) model that estimates ambient NO2 concentrations at any location in Ireland with particular emphasis on vehicle fleet changes and traffic flow impacts on NO2.

Research 440: Advances in Sustainable Nutrient Recovery for the Management of Nitrogen-rich Residue Streams (REFERT)
Authors: Bart Bonsall, Donncha Haverty, Corine Nzeteu, Pádraic Ó hUiginn and Vincent O’Flaherty, November 2023
Year: 2023
Across the EU, anthropogenic sources of nitrogen (N) threaten water and air quality. Agriculture is also a significant source of N and GHG emissions linked to climate change. N for crops is sourced from mineral fertilisers, livestock manures and anaerobic digestion digestates. Landfill leachates also generate N and GHG emissions. The EPA funded this research to identify cost-effective methods to mitigate the release of N and GHGs from ammoniacal streams.

Research 439: Research on the Environment, Health, Consumer Behaviour and the Economy: ESRI Research Programme on Environmental Socio-economics 2020–2022
Authors: Ylva Andersson, Peter Barlow, Philip Carthy, Kelly de Bruin, Míde Griffin, Seán Lyons, Pete Lunn, Bertrand Maître, Likun Mao, Maria Martinez Cillero, David Meier, Gretta Mohan, Kieran Mohr, Anne Nolan, Brian O’Connell, Vincent O’Sullivan, Aidan Sloyan, Shane Timmons, Miguel Tovar Reaños, Brendan Walsh and Aykut Mert Yakut, October 2023
Year: 2023
The main objective of this EPA-ESRI collaboration is to produce policy-relevant applied research at the interface between the environment, economy, and society. This report provides a summary of 12 studies, produced by the ESRI, that use a range of data and methodological approaches to provide insights into the environmental challenges facing Irish society. The studies include analyses of the impact on healthcare systems from the smoky coal ban, living in areas of higher PM2.5 levels, e-coli exceedances in drinking water and water related diseases in the summer months. It also examines the potential for a “green VAT”, the levels of emissions embedded in imports and the best ways to present information to people to enable action.

Research 430: Sources, Pathways and Environmental Fate of Microplastics
Authors: Roisin Nash, John O’Sullivan, Sinead Murphy, Michael Bruen, Anne Marie Mahon, Heather Lally, Linda Heerey, James O’Connor, Xiaodi Wang, Albert Koelmans and Ian O’Connor, March 2023
Year: 2023
As plastic production continues to increase, we are seeing significant quantities of microplastics (MPs), a contaminant of emerging concern, being recorded worldwide. This research project has identified key challenges and recommendations that target MP pollution, highlighting immediate measures that could manage MP debris at known sources. This will inform the development and implementation of policies such as the Water Framework Directive.

Research 427: Fungal Monitoring Network and Algorithm
Authors: David O’Connor, Jerry Hourihane Clancy, Moisés Martínez-Bracero, Eoin McGillicuddy and Emma Markey, December 2022
Year: 2022
Bioaerosols are biological particles in the air such as pollen, fungal spores, bacteria and viruses. While most are harmless, some can trigger adverse effects such as hay fever or respiratory diseases. The impacts of bioaerosols on the health of the Irish population and agriculture and the linkages to climate remain underexplored. This project seeks to address this problem by undertaking the required monitoring and by developing a forecast model.

Research 423: Environmental Transport Noise and Health: Evidence from Ireland (Noise–Health)
Authors: Enda Murphy, Jon-Paul Faulkner, Ciarán Mac Domhnaill, Seán Lyons, Anne Nolan and Owen Douglas, September 2022
Year: 2022
Noise is found everywhere, particularly in urban areas, and is part of daily living and activity. However, noise can be a serious risk to public health and wellbeing. This report outlines key policy and practice recommendations for managing environmental noise in Ireland. It also details how “noise–health” considerations can be better incorporated into Irish policy.

Research 420: Pollen Monitoring and Modelling (POMMEL)
Authors: David O’Connor, Emma Markey, Jose Maria Maya-Manzano, Paul Dowding, Aoife Donnelly and John Sodeau, August 2022
Year: 2022
A reliable pollen forecast and monitoring system is a valuable tool to help allergy sufferers avoid unnecessary exposure to allergenic pollen and to optimise drug treatments by allergists. Ireland does not have a monitoring system in place and the forecast currently used is provided by the University of Worcester (UK). This project seeks to address this by undertaking the required monitoring and developing a forecast model.
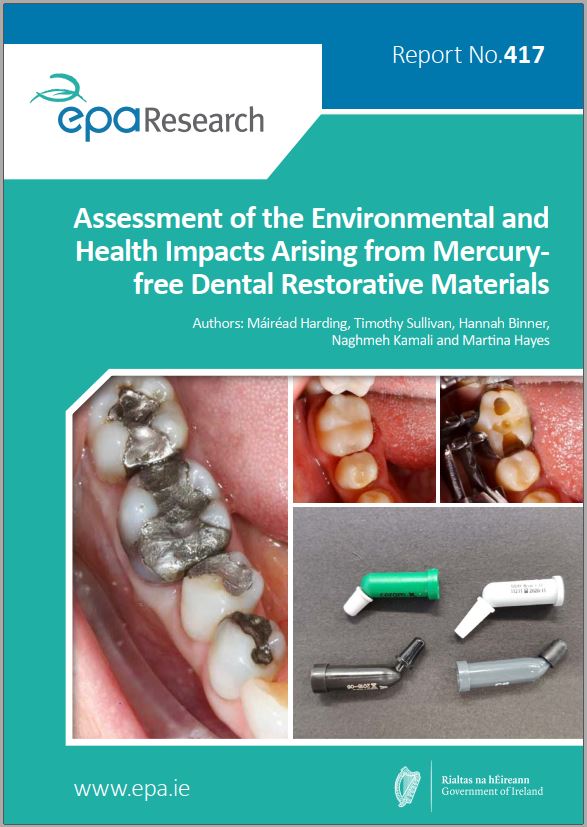
Research 417: Assessment of the Environmental and Health Impacts Arising from Mercury-free Dental Restorative Materials
Authors: Máiréad Harding, Timothy Sullivan, Hannah Binner, Naghmeh Kamali and Martina Hayes, July 2022
Year: 2022
The United Nations Minamata Convention on Mercury is an international regulatory framework that aims to protect human health and the global environment from the harmful effects of mercury. This research identified that very little literature exists on the environmental and health impacts of mercury-free dental restorative materials. It identified small particles from the mercury-free dental restorative materials in dental wastewater (DWW) and says it is essential to consider enhanced capture of small particles from DWW as a priority.

Research 416: Development and Application of Monte Carlo Models for High-purity Germanium Gamma Spectrometry
Authors: Luis León Vintró and Niall Murphy, July 2022
Year: 2022
The aim of this research project was to develop and implement suitable Monte Carlo calibration methods for the assay of natural and artificial radionuclides using HPGe gamma spectrometers. A software application was developed as part of this project. The application makes use of a set of nominal input parameters describing an HPGe detector, together with experimentally determined full-energy peak efficiencies for a range of radionuclides in a variety of counting geometries, to produce an optimised model of the detector by applying suitable optimisation algorithms without any further user intervention.

Gap analysis of research needs to understand the environmental dimension of antimicrobial resistance in preparation for iNAP2
Authors: Niamh Cahill, Dearbháile Morris, Finola Leonard, Fiona Walsh, December 2021
Year: 2021
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) is one of the greatest global threats we are facing in today’s world. As recognised in Ireland’s first National Action Plan on Antimicrobial Resistance, adopting a One Health approach is key to effectively tackling the problem of AMR. A comprehensive analysis of previous and ongoing research relating to the occurrence, risk, fate and transport of antimicrobial residues and AMR to and within the environment was completed.
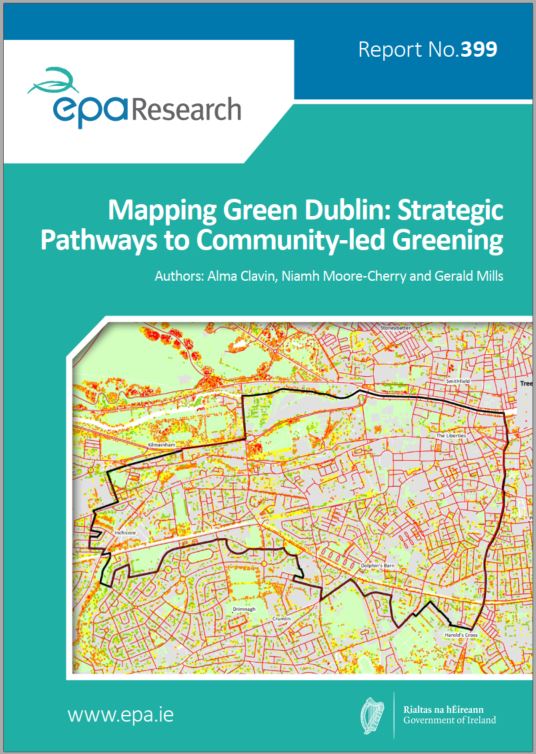
Research 399: Mapping Green Dublin: Strategic Pathways to Community-led Greening
Authors: Alma Clavin, Niamh Moore-Cherry and Gerald Mills, December 2021
Year: 2021
Enhancing green infrastructure in densely populated centres is an important means of improving urban environments, with benefits for air and water quality, as well as biodiversity enhancement. The project Mapping Green Dublin examined the variable green cover in the Dublin City Council area. It has generated data on the city’s trees, identified those places with significant environmental deficiencies and worked with the local community to develop a greening strategy for the Dublin 8 area. Mapping Green Dublin has established a process for effective engagement with neighbourhoods that allows residents to be participants in the design of their own spaces.

Research 383: Towards a Good Practice Guide for Implementing CNOSSOS-EU (Common Noise Assessment Methods in Europe) in Ireland
Authors: Jon-Paul Faulkner, Enda Murphy, Henry J. Rice and John Kennedy, June 2021
Year: 2021
This guide addresses noise pollution from transport as a significant environmental pressure and public health concern. The guide is primarily targeted at practitioners charged with implementing the 5-yearly strategic noise mapping requirements of the Environmental Noise Directive (END). The guide also supports relevant authorities by providing robust analysis and instruction on how to implement strategic noise mapping under CNOSSOS-EU.

Research 382: Transitioning to Strategic Noise Mapping under CNOSSOS-EU (Noise-Adapt)
Authors: Enda Murphy, Jon-Paul Faulkner, Henry J. Rice and John Kennedy, June 2021
Year: 2021
In the European Union (EU), 113 million people are estimated to be exposed to noise pollution from transport sources and this is detrimental to their health and quality of life. This report addresses noise pollution from transport as a significant environmental pressure and public health concern by providing recommendations that assist with the practical implementation of revisions to the Environmental Noise Directive.

Research 377: Impacts of Microplastics in the Irish Freshwater Environment
Authors: Alicia Mateos-Cárdenas, Alexandra R.J. Jansen, John O’Halloran, Frank N.A.M. van Pelt and Marcel A.K. Jansen, June 2021
Year: 2021
Plastics are a key part of modern life, due to their desirable characteristics such as light weight and low cost. However, the extensive production of plastics is resulting in plastic pollution. This study recognises the risk posed by rapid formation of micro- and nanoplastics in the freshwater environment and advocates the rapid development of field-monitoring and impact studies to analyse hazards and risks posed by these plastics.

Research 370: Potential Health Impact of Phthalates: An Irish Perspective
Authors: Catherine Allen, Fiona Regan, Anthony Staines and Jenny Lawler, April 2021
Year: 2021
Phthalates are plasticisers that are ubiquitous in the environment, have the potential to disrupt the endocrine system and are associated with a wide range of adverse health effects. This report identifies that all 11 phthalates studied are currently present in the Irish environment. The levels of human exposure indicate that there is no immediate risk to human health on a population-averaged basis.

Research 361: The State of the Art on the Potential Human Health Impacts of Microplastics and Nanoplastics
Authors: Imen Gdara, Jenny Lawler, Anthony Staines and Sandra O’Neill , January 2021
Year: 2021
Human exposure to microplastics and nanoplastics through inhalation, ingestion and dermal exposure is an emerging health concern. Designing studies to assess the health effects of these exposures is challenging. Until these studies are conducted, governments should revise directives and policies on food, water and air to include MPs/NPs, to remove the potential for plastic to contaminate the food chain and our environment.